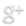On 25 April and 12 May 2015, deadly earthquakes struck central Nepal, causing catastrophic damage to Kathmandu and the surrounding valleys. Harrowing pictures of magnificent temples turned to rubble and concrete hotels collapsed on their foundations were beamed around the world. Five months on from the disaster, Nepal has declared itself open for tourism, but is now the right time to come back to Nepal, and what exactly will you find when you get here?
Assessing the damage
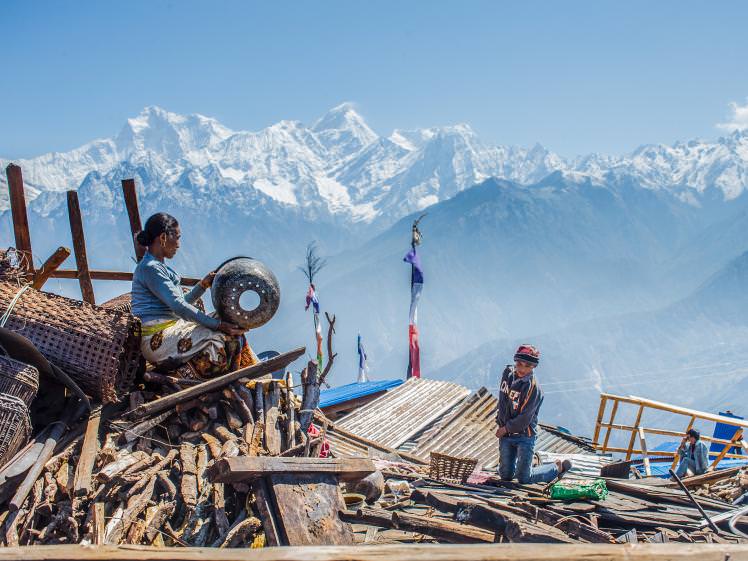
Media images at the time of the earthquakes made it look as though Nepal was completely destroyed, with its astonishing cultural heritage in ruins. The truth makes for less sensational headlines: while 130 historic temples collapsed across the country, only 14 of Nepal’s 75 districts suffered damage, and many of Nepal’s most famous sights escaped completely unscathed.
Even at the height of the disaster, travellers were relaxing in the resort town of Pokhara, unaware of the destruction to towns just 50km away. In Kathmandu, the vast majority of hotels reopened within days of the earthquakes, with just a handful of historic heritage hotels remaining closed for repairs.
This is not the first time Nepal has faced an earthquake of this scale, and as in 1934, Nepalis have stepped in to save what can be saved, and are now rebuilding for the future. How quickly this can happen will depend to a large degree on how quickly tourists return to the country and invest in the local economy.
Here is an overview of how different parts of Nepal are recovering after the disaster.
Kathmandu suffered the full force of the earthquakes, and damage was extensive, but localised to specific parts of the city. Four of the iconic temples in the UNESCO-listed Durbar Square collapsed completely including the multi-tiered Maju Deval Temple, one of Kathmandu’s most famous landmarks but the majority of temples still stand and the square is once again open to sightseers.
The royal palace of Hanuman Dhoka remains closed due to structural damage to the southern courtyards, but work is underway to reopen the museum and palace chambers. Perhaps the most photographed casualty of the earthquake was the Bhimsen Tower, which collapsed completely for the second time in its history (it was also destroyed in the 1934 earthquake). Today, it stands as a ruined plinth, but developers have pledged to rebuild it.
Other major World Heritage Sites such as the magnificent Buddhist stupas at Swayambhunath and Bodhnath were only mildly affected; restoration work has repaired the most obvious damage and the most tangible evidence for the disaster is some lingering scaffolding. The sacred Hindu pilgrimage site of Pashupatinath saw a terrible tide of funeral cremations following the earthquake but the site itself was mostly undamaged.
Patan, Bhaktapur & the Kathmandu Valley
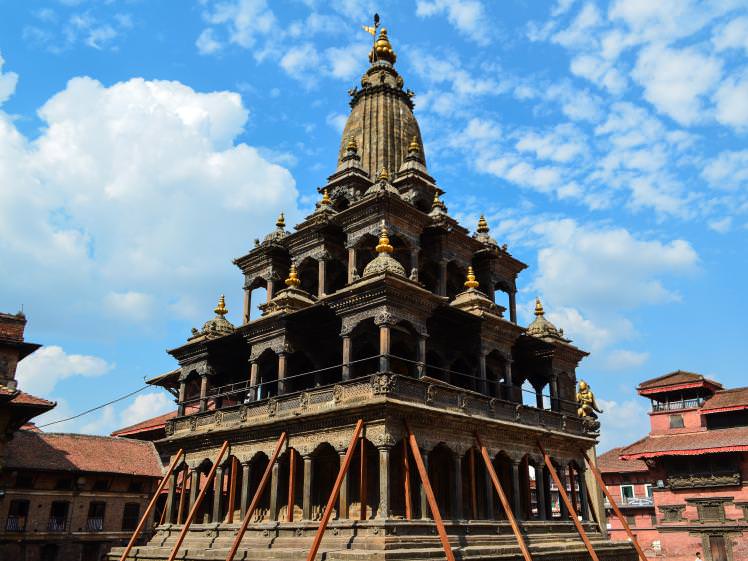
Despite the loss of some landmark monuments, including the famous Char Narayan and Hari Shankar temples, Patan’s Durbar Square and its stunning Patan Museum are open as normal. The quakes took a heavy toll on the traditional brick buildings of Bhaktapur, but here too, most of the medieval temples are still standing, including Nepal’s tallest, the five-storey Nyatapola Temple.
Elsewhere in the Kathmandu Valley, the damage was patchy. Some places escaped with minor cracks, while towns like Sankhu and Bungamati saw temple after temple crumble to rubble. While the valley is definitely open to travellers, it’s worth checking with locals before heading off from Kathmandu to be clear on which areas are still off-limits due to reconstruction following the disaster.
Across the country
Looking beyond the Kathmandu Valley, the historic towns of Nuwakot and Gorkha and their fortress-palaces were particularly badly affected due to their proximity to the epicenters of the two tremors, and the quakes caused extensive damage to the road to the Tibetan border and the Langtang Valley. However, away from the center of the country, there are few signs that the earthquake ever happened.
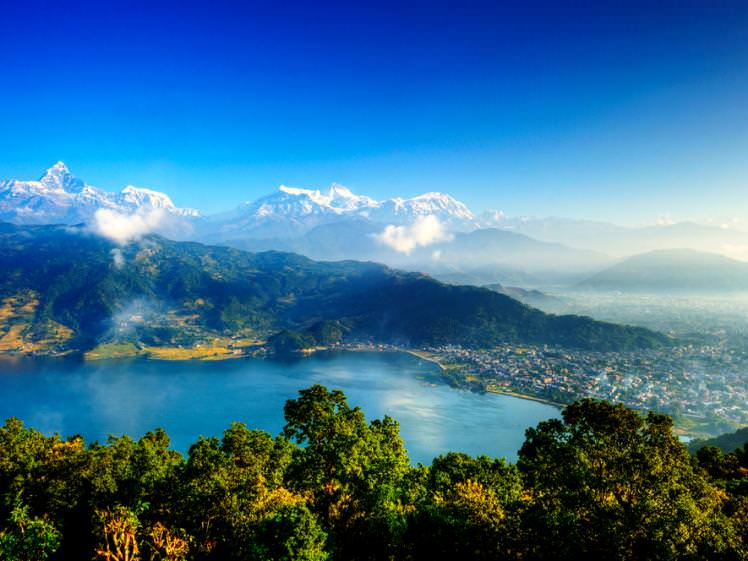
The east and west of the country were not seriously affected by the disaster, and most damage is restricted to trekking routes in remote areas. The tourist and trekking hub of Pokhara was effectively untouched and the trekking routes around it have been surveyed and declared safe. Despite damage to some villages along the trails, trekking in the Everest region has also been declared safe.
In the lowlands, the towns and national parks of the Terai were almost entirely unaffected. Wildlife safaris in Chitwan National Park and Bardia National Park continue as normal and the number of tigers in Nepal is actually on the rise, bucking the regional trend. The birthplace of the Buddha at Lumbini – an increasingly popular stop on the overland route between India and Nepal – also escaped unharmed.

Image by Chris Marquardt
Travelling to Nepal after the earthquake
The key thing to note is that infrastructure for tourists was remarkably unaffected by the disaster. Airports are operating as normal and almost all of Kathmandu’s tourist hotels and restaurants remain open, or will reopen for the winter tourist season, though business is currently slim. Kathmandu’s traveller district of Thamel is much as it was before the disaster, and transportation around the city, the Kathmandu Valley and the country continues as normal.
The main roads across Nepal are open to traffic (or as open as they ever were!), and the Arniko Hwy/Friendship Hwy to Tibet and Everest’s North Base Camp (in Tibet) is due to reopen for the 2015 winter season. However, roads are still cut off in some rural areas, where earthquake damage has been worsened by monsoon landslides. This situation is likely to persist for some time, so it pays to confirm that roads are clear and that accommodation will be available before leaving Kathmandu.

Image by Wonderlane
So should I go ?
In August, the US and UK lifted their country-wide travel advisories against travel to Nepal, meaning that travellers and companies can once again get travel insurance for upcoming trips. Most western travel companies plan to run trekking trips as normal for the 2015/16 winter and spring seasons and some companies are even offering special reconstruction treks, though it’s now more important than ever to do some research and partner with a reliable NGO that has long-established links with the country.
Of course, Nepal still has its problems – including a fuel shortage caused by a political stand-off with India over the new Nepali constitution – but these kinds of issues are part of the landscape when travelling in the subcontinent. Despite these problems, in many ways now is a great time to visit Nepal.
The infrastructure that travellers need is in place, but tourism is down by over 50%, which means fewer crowds on the popular trekking routes and discounts for hotels and airfares. More importantly, the money you spend when hiring a guide or porter, staying in a lodge or hotel, or eating in a restaurant will directly help local people. Given that 500,000 Nepalis work directly in tourism, the country needs travellers more than ever to rebuild its economy and bounce back stronger for the future.
Follow and share our more detail from our social media ; Facebook, Pinterest and Twitter.
Source: www.lonelyplanet.com
Contact Us:
E-mail: sales@samratnepal